Compliance
HIPAA technical safeguards explained for your small practice

Estimated reading time: 13 minutes
HIPAA technical safeguards are like the digital locks and keys of your practice’s electronic protected health information (ePHI) — such as emails, digital records, and health data you store, access, send, or receive electronically. They're the security measures that protect sensitive health information from falling into the wrong hands.
Most resources out there will leave you drowning in technical terms or skimming the surface with vague generalities. If the thought of audit controls and encryption for your small practice overwhelms you, bookmark this guide and share it with a friend who runs a practice, too!
Keep reading to learn about HIPAA's technical safeguards in the context of small healthcare practices. We'll also share practical solutions tailored for you — clear, simple steps that you can easily implement to protect your clients and give yourself peace of mind.
What is the purpose of HIPAA technical safeguards?
HIPAA technical safeguards include a range of technologies and practices designed to prevent unauthorized access to, alteration of, or destruction of electronic protected health information (ePHI). These safeguards also ensure the secure transmission of ePHI and protect it during transfer.
In simpler terms, they ensure that only the right people can see and use client data and that it remains accurate and intact. Just like you wouldn't leave your office door unlocked overnight, you wouldn't want your practice's digital client information vulnerable to unauthorized access.
What do these technical safeguards have to do with the HIPAA Security Rule?
The HIPAA Security Rule is the backbone of these technical safeguards. It's a set of federal requirements that mandate healthcare providers to implement measures to protect ePHI. The Security Rule applies to all forms of ePHI, whether stored on systems like computers, phones, and tablets or transmitted electronically in any way.
The HIPAA Security Rule requires practices to implement the following:
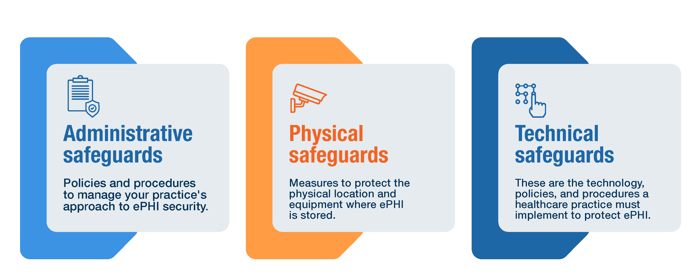
- Administrative safeguards: Policies and procedures to manage your practice's approach to ePHI security.
- Physical safeguards: Measures to protect the physical location and equipment where ePHI is stored.
- Technical safeguards: These are the technology, policies, and procedures a healthcare practice must implement to protect ePHI. 👉 The focus of this guide. We'll delve deeper into the technical safeguards you should know, and how to implement them in your small practice.
Required vs. addressable implementation specifications
Before we take a detailed look at the technical safeguards, it's worth noting that within each HIPAA Security Rule standard, there are specific actions or measures called implementation specifications that help you achieve HIPAA compliance.
These implementation specifications fall into two categories:

- Required: These are mandatory. You must implement these specifications to be HIPAA compliant in your healthcare practice.
- Addressable: While these aren't strictly mandatory, they are not optional either. You need to assess each one to determine if it's "reasonable and appropriate" for your practice.
What does "reasonable and appropriate" mean?
It depends on a number of factors, as documented in your practice’s Risk Assessment Analysis, including the:
- Size and complexity of your practice
- Nature of the ePHI you handle
- Available resources (budget, technology, personnel)
- Potential risks and vulnerabilities
If an addressable specification isn't a good fit, what then?
You can implement an alternative measure that still achieves the purpose of the standard. This alternative must also be reasonable and appropriate for your situation. For example, an addressable specification might recommend encrypting ePHI. A large hospital system might deploy a comprehensive encryption system across all platforms, while a small healthcare practice could take an alternative approach by using encryption for email and electronic health records, implementing strong passwords, and enabling two-factor authentication. Both approaches aim to protect the confidentiality of ePHI, but the implementation varies based on the organization's resources and capabilities.
HIPAA recognizes that a small practice like yours has different needs and resources than a large hospital system. The "addressable" specifications allow you to tailor your security measures to your specific circumstances and protect ePHI without overcomplicating your operations or breaking the bank.
However, an important note: you must document your decisions as part of your Risk Assessment and mitigation strategy.
|
👉 If you decide not to implement an addressable specification, you must explain why and document the alternative measures you've adopted. This demonstrates your due diligence in protecting ePHI. |
Even though addressable specifications offer some leeway, taking them seriously is essential. Ignoring them would leave your practice vulnerable to security breaches and HIPAA violations.
Now that we've cleared that up, let's explore some of the key technical safeguards and their implementation specifications in the following sections. This will help you make informed decisions for your practice.
What are the HIPAA technical safeguards?
The HIPAA technical safeguards act like a foundational fortress to your ePHI. These include the following:

- Access controls: Ensuring only those authorized can access ePHI and keeping everyone else out.
- Audit controls: Monitoring and recording who accessed ePHI and when.
- Integrity: Ensuring ePHI remains accurate and unchanged.
- Person or entity authentication: Verifying the identity of those accessing ePHI.
- Transmission security: Protecting ePHI during transmission.
1. Access Controls: Ensuring only those authorized can access ePHI, keeping everyone else out.

This technical safeguard ensures that only authorized individuals, like you and those of your staff who are permitted, can access ePHI. It may look like this in your practice:
Must-haves (Required)
- Unique user identification: Think of this like a personalized keycard for each staff member. It tracks who's accessing what, making it easier to spot any unusual activity.
- Emergency access: Even in a crisis, you need a way to obtain your practice's ePHI. This means having a plan for accessing records if your systems go down (like during a power outage).
Addressable
- Automatic Logoff: Like a door that automatically closes, this feature logs out users after a period of inactivity, preventing unauthorized access if someone forgets to log out.
- Encryption: Imagine scrambling your ePHI into a secret code, so even if someone manages to get their hands on it, they can't read it without the key (decryption). It's especially important if you're sending information electronically.

Your action plan
- If you have staff, ensure they have unique usernames and passwords before they can use any computer with access to client information.
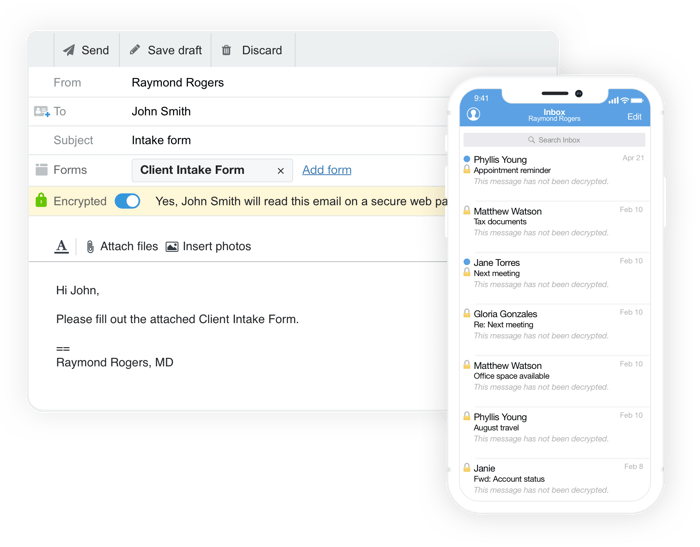
- Use a HIPAA-compliant email service with built-in encryption designed for healthcare practices like Hushmail for Healthcare.
- Enable Touch ID or Face ID on your devices if available.
- Encrypt your phone or device through its security settings.
- For iPhones, check the "Encrypt local backup" option when backing up.
- Set strong passwords, PINs, or patterns, and enable automatic screen locking.
- If you use cloud storage, make sure it offers encryption.
- Use secure web forms such as Hush™ Secure Forms.
- Regularly review who has access to your practice’s data and revoke access for anyone who no longer needs it.
- Conduct a HIPAA risk assessment.
- When someone leaves your practice (employee, contractor, etc.), immediately remove their access to your computer systems, email, and other practice resources. See this list for further guidance.
- Have a clear plan for handling emergencies that might affect your access to client information and disrupt normal operations. This plan will ensure your practice can continue providing care and quickly recover from disruptions like a power outage, system failure, or security breach. See this list for further guidance.
|
👉 Important note: While the Action Plan section provides suggested items and examples to get you started, you must tailor your plan based on a thorough risk assessment of your practice's specific needs and vulnerabilities. |
2. Audit controls: Monitoring and recording who accessed ePHI and when.

This HIPAA technical safeguard is like a watchful eye on who's accessing what and when so you can spot any unusual activity.
You need a system to record all activity related to your practice's ePHI. This standard has no implementation specifications, meaning you have some flexibility in setting this up as long as it achieves the goal of tracking activity. This typically includes:
- Who logged in and out of your system
- Any failed attempts to access information
- When someone views, creates, edits, or deletes ePHI
Here's an example scenario:
Imagine receiving a security alert from Google notifying you of a suspicious login attempt. Perhaps someone tried to access your Google Drive files from an unfamiliar location or device. This alert lets you immediately investigate the situation, change your password if needed, and take further steps to secure your account. By enabling and monitoring these security alerts, you're proactively protecting your client's sensitive information and maintaining control over who can access it.
Your action plan
1. Know what to watch for
- Identify which computer programs store sensitive client information (like names, appointments, and notes).
- Decide which actions to track (e.g., who logged in, viewed, edited, or deleted files).
- Check if your existing programs have security alerts enabled. Here’s an example of how it works in Google Drive.
2. Find ways to track changes
- Enable any tracking features (if available) in the software or programs you're using at your practice.
- If you print client notes, jot down who accessed them and when. A notebook works fine.
- Make sure these logs are stored safely, just like your client files.
3. Check the logs regularly
- Decide how often it is reasonable to check (e.g., once a week, once a month).
- Look for anything unusual (e.g., someone logging in at odd hours or accessing files they shouldn't).
- If you find anything suspicious, take action immediately (change passwords, contact tech support).
3. Integrity: Ensuring ePHI remains accurate and unchanged.

Integrity, as a technical safeguard, ensures your ePHI stays accurate and unchanged. It's like having a tamper-proof seal on an envelope that can reveal if someone's tried to alter the contents.
Must-haves (Required)
- Protect from changes: You need to make sure no one, intentionally or unintentionally, changes or deletes ePHI without being authorized to do so.
Addressable
- Authentication Mechanisms: These are like digital alarms that go off if someone tries to alter the data. These might include features like:
- Confirmation prompts before deleting or modifying records.
- Using checksum verification (a techy way to check if data has been altered) during your regular security audits.
For example, let's say you're using an online platform to store client therapy notes. This platform might use checksums to verify the integrity of your files. Every time you save a note, the platform takes a snapshot. This snapshot is the checksum. Later, if you open that note and the platform notices the 'snapshot' doesn't match, it could mean the file was accidentally changed or corrupted. Maybe a software glitch scrambled some of the text, or perhaps your computer crashed while saving the file. This mismatch alerts you to a potential problem, allowing you to investigate and potentially restore a previous version of the note, ensuring your records remain accurate and complete.
Your action plan
- Keep documents confidential and only share them with the right people. When sharing documents, always verify that the recipient is authorized to receive them. If you're using Google Drive, learn how to tighten sharing requirements in Google Drive.
- Regularly back up your data to have a clean copy if something goes wrong. If you're a Hushmail for Healthcare user, you automatically benefit from an archive account that maintains a separate record of all emails sent and received within your domain. This provides an extra layer of protection for your client communication.
- Conduct periodic reviews of access privileges to remove unnecessary permissions and prevent unauthorized access.
- Set up your EHR system (if you're using one) to control who can see and change your clients' ePHI.
- Implement a regular backup schedule to create copies of ePHI and store them in a secure location.
- Keep your tech updated. Make sure your computer, phone, and any practice software are always up-to-date.
- Protect your devices with antivirus and anti-malware software. These tools will scan for and remove any threats.
- If you find any problems or threats during your regular check-ups, fix them immediately.
- If you or your staff work remotely, avoid using public Wi-Fi. It's not as secure as your home or office network.
4. Person or Entity Authentication: Verifying the identity of those accessing ePHI.

Person or entity authentication ensures the right people have the keys to your digital "office." It ensures that anyone trying to access ePHI is authorized to do so.
Must-have (Required)
- Verify identity: You must have a way to confirm that any individual trying to access your practice's ePHI is legitimate and authorized to do so.
Your action plan
- Use strong, unique passwords for each account, and consider using a password manager to keep them secure.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), which adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. Also known as two-step verification, it requires a second piece of information, like a code from your phone and your password. This prevents unauthorized access even if someone knows your password.
- If it makes sense for your practice, consider using fingerprint or face scans to verify who's accessing your computer systems. This adds an extra layer of security by making it much harder for unauthorized people to get into your files.
- Create unique logins for you and each staff member. Use unique credentials. See this list for further guidance.
- Keep regular accounts separate from accounts with special access rights. See this list for further guidance.
- Regularly remind your staff to keep their login information private, never share it with anyone, and update their passwords periodically.
5. Transmission security: Protecting ePHI during transmission.

Let's say your client's ePHI is like a valuable package being shipped. You wouldn't want it sent in a flimsy box that anyone could open, right?
Transmission security is like using a secure shipping box with tamper-evident seals and tracking. It ensures your clients' sensitive data is protected and can't be intercepted, changed, or read by anyone else during its journey (sent electronically).
Must-have (Required)
- Guard against unauthorized access: You must ensure no one can intercept, change, or read ePHI while it's being sent electronically (through email or over the internet).
Addressable
- Integrity controls: As mentioned earlier in safeguard #3 (Integrity), these help to maintain the accuracy of ePHI during transmission by ensuring it hasn’t been altered. It's like adding a special seal to your envelope that shows if it's been opened.
- Encryption: This is the digital equivalent of scrambling your message into a secret code. Even if someone intercepts it, they can't read it without the key (decryption).
Your action plan
- Choose a HIPAA-compliant email, like Hushmail for Healthcare, with encryption to protect your client's information.
- Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN creates a secure, encrypted "tunnel" for your internet traffic, making it much harder for anyone to intercept or access your data in transit. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi, which is often unsecured.
- Be cautious of attachments. Avoid opening suspicious attachments or clicking on links from unknown senders. Suspicious attachments may contain viruses or malware that could compromise your entire system, potentially exposing client information during transmission or while stored on your devices.
- Ensure everyone in your practice understands the importance of email security and knows how to spot potential threats through regular training.
- Make sure that the companies you work with also have good online practices. See this list for further guidance.
- Use secure forms as an alternative to fax.
- For encryption guidance, follow these steps.
Do you need to comply with the HIPAA technical safeguards?
Even though your practice is small, you handle sensitive client information, which makes you responsible for protecting it under HIPAA.
Here are some key points to remember:
- Data breaches happen, even to small practices. The data shows that small and large organizations struggle with technical safeguards and face breaches. If you suffer a breach that affects 500 or more individuals, you will face an investigation and appear on the HIPAA Wall of Shame.
- The consequences can be serious. If your practice's data is compromised, you could face hefty fines, lawsuits, a corrective action plan, and damage to your reputation. It's just not worth the risk.
- New guidelines are coming. The government plans to introduce HIPAA Security Rule updates that focus on preventing cyberattacks and data breaches. By implementing HIPAA technical safeguards now, you'll be ahead of the curve and ready to meet these new requirements.
Start with small, manageable steps in implementing HIPAA's technical safeguards at your practice.
HIPAA's technical safeguards are more than just checking boxes for compliance; they're about building a secure foundation for your practice and safeguarding your clients' sensitive information.
You don't have to become a tech expert overnight! Start with small, manageable steps, like choosing a HIPAA-compliant email provider like Hushmail for Healthcare. Every step you take, no matter how small, contributes to a more robust security posture for your practice.
Overwhelmed by the business side of private practice? In this guide, therapists share 20 ways they've offloaded what drains them, to create more space for the work they love.




